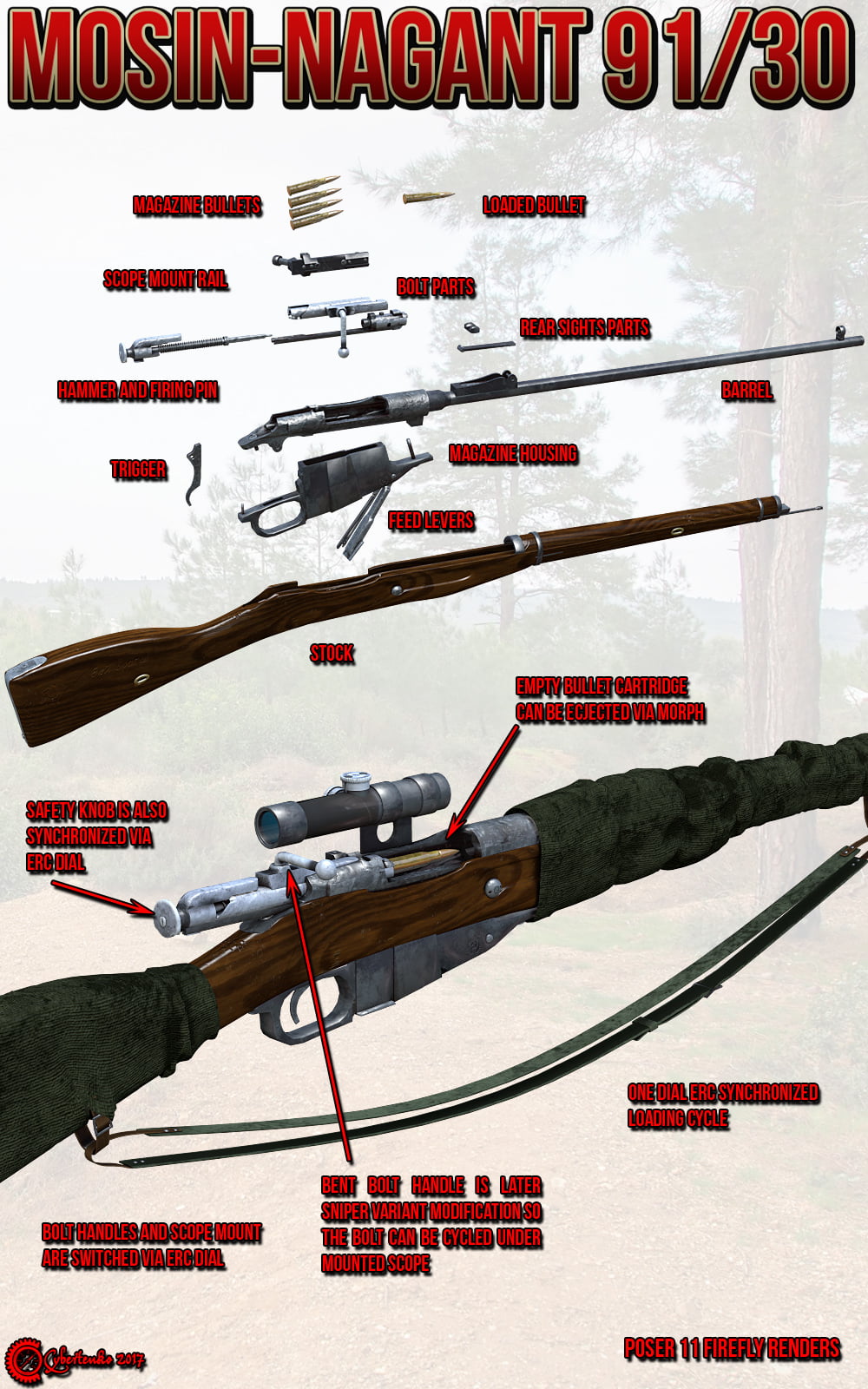
The Mosin–Nagant is a five-shot, bolt-action, internal magazine–fed, military rifle developed by the Imperial Russian Army from 1882 to 1891, and used by the armed forces of the Russian Empire, the Soviet Union and various other nations. It is one of the most mass-produced military bolt-action rifles in history with over 37 million units having been made since its inception in 1891, and, in spite of its age, it has been used in various conflicts around the world even up to the modern day, being plentiful, cheap, rugged, simple to use, and effective.
The Mosin–Nagant Model 1891/30 was modified and adapted as a sniper rifle from 1932 onwards with mounts and scopes from Germany at first and subsequently with domestic designs (PE, PEM) and from 1942 was issued with 3.5-power PU fixed focus scopes to Soviet snipers. It served quite prominently in the brutal urban battles on the Eastern Front, such as the Battle of Stalingrad, which made heroes of snipers like Vasily Zaitsev and Ivan Sidorenko. These sniper rifles were highly respected for being very rugged, reliable, accurate, and easy to maintain.